interoperability
What we do
We collaborate with countries to design, develop, test, and implement health interoperable frameworks and applications using international digital health architecture, standards, and emerging technologies. As such, we support countries achieving Universal Health Coverage, the third sustainable development goal.


the challenge
Clinicians need accurate, timely, and complete information for decision-making but healthcare information solutions often exist in siloes, making it difficult to share information across different systems. This undermines the impact of healthcare workers and affects their ability to deliver quality work, losing significant time in addressing data errors and completing reporting requirements.
ARCHITECTURE DEFINITION
We dress the status of your digital framework and understand your digital challenges to define together the architecture of the interoperable system answering your information gap.

ITERATIVE DEVELOPMENT
We work hand in hand with you from the development of the repositories, mediators and interfaces/ information exchange system to the implementation and the iterative quality insurance events.
TECHNOLOGY TRANSFER
We conduct technology transfer all along so that local organizations can leverage, extend and sustain the information exchange system.
your benefits

unique identification
Enable the patient identification standardization, the merging of patient duplicates facilitates the exchange of patient information from disparate systems to one care record.
Asset and resource optimization
Reduce the data manager workload by avoiding redundantly data capture. identifying current capacity, modelling future demand to reduce asset and resource wastage.
Informed care decision
Access the entire patient medical history guides the clinician to better stratify patient health conditions and take the right decision accordingly.

Easier collaboration
Standardized, reliable and consistent data eases significantly the automation of reporting reducing the turnaround time to receive urgent information across programs or services

Smooth transfer of care
Allow a transparent transfer of accurate and comprehensive information between and within care settings facilitates the follow-up of patients through the different steps of the continuum of care and the expansion of care coverage.
Centralized security management
Secures and facilitates the monitoring of data transition between systems such as control of user access, auditing of errors.
Case study
Rwanda Health Information Exchange System (RHIES)

Read more
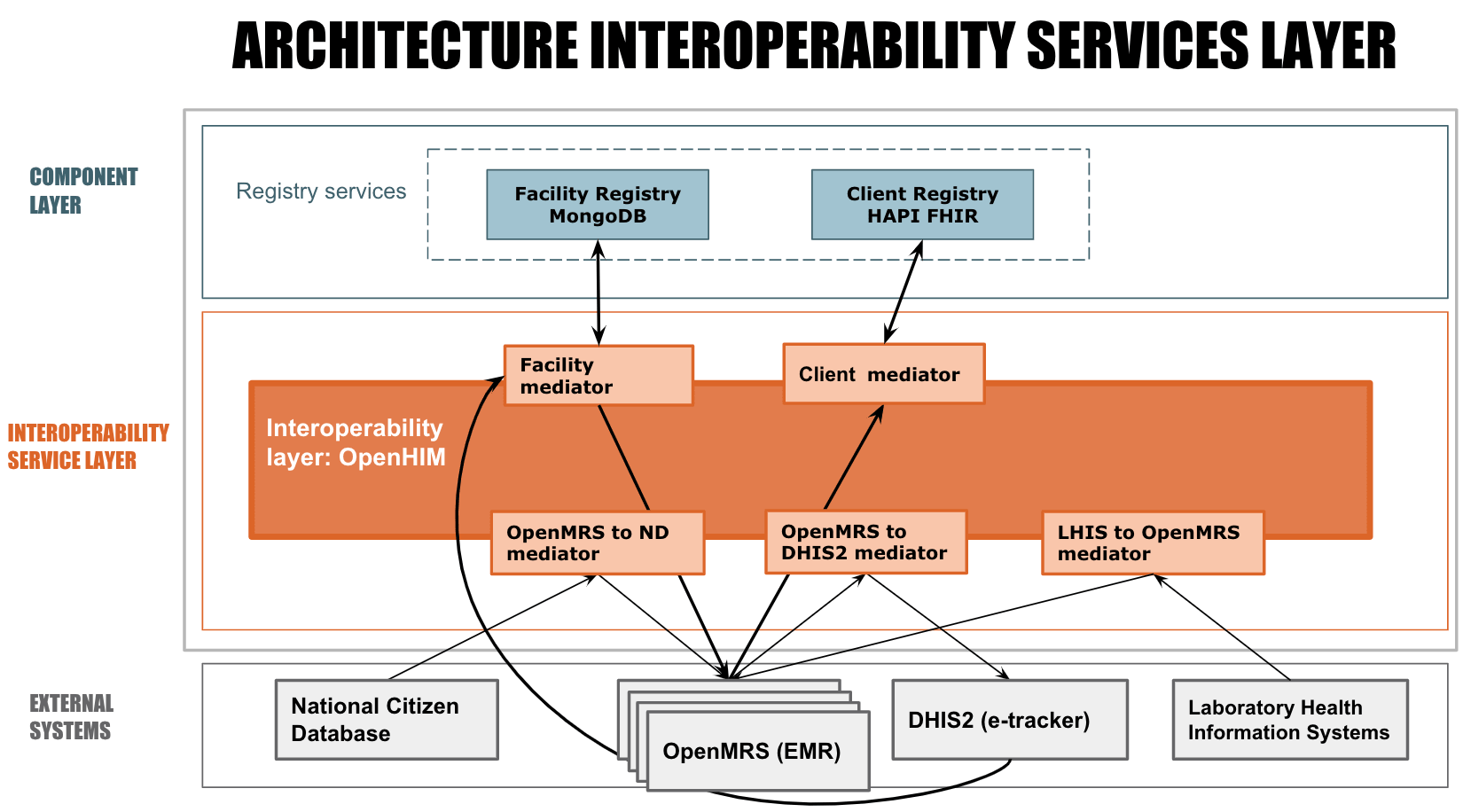
Together with the Rwanda Biomedical center, we have developed the Rwanda Health Information Exchange System (RHIES). RHIES is a set of applications connected via a centralized interoperability services layer aligned with the Open Health Information Exchange (OpenHIE) architecture to serve point-of-service systems such as EMRs, DHIS2, National ID database and laboratory information systems. We also have developed a Facility and Client registry which serves as central authority for maintaining the unique identities of places where health services are administered and of citizens receiving health services within the country.
A Health Information Exchange (HIE):
The shared infrastructure represented by the large gray box in the diagram, makes the sharing of health data across information systems possible.
Interoperability Services Layer:
A software component that enables easier interoperability between disparate electronic information systems by providing a central point where the exchange of data is managed. An interoperability layer receives transactions from different information systems and coordinates the interactions between them.
Mediators
Verification of the credentials of systems sending messages to the interoperability layer.
The External systems
Represent applications or systems that are such as the OpenMRS electronic medical records (EMR) system, Laboratory information system, DHIS2, national citizen identification database (NIDA) used by clinicians, data managers and community health workers to access and update a patient’s person-centric shared health information and to record other healthcare transactions.
Registry Services are Health Exchange Components that are designed to support registries with data that is used by other Health Exchange components.
- Client Registry manages the unique identity of citizens receiving health services with the country – in our case directly connected to the national citizen database
- Facility Registry serves as a central authority to uniquely identify all places where health services are administered within the country and the related information (location, services available, coordinates, etc)